Introduction to Algebra
Algebra is one of the most fundamental branches of mathematics, serving as the backbone for advanced mathematical studies, science, engineering, computer science, economics, and everyday problem-solving. Unlike arithmetic, which focuses on numbers, algebra introduces variables, symbols, and generalized relationships that allow us to model real-world situations efficiently.
Whether you are studying pre algebra, algebra 1, algebra 2, linear algebra, or advanced systems like algebra Boole, binary algebra, and magma algebra, algebra helps build logical reasoning and analytical thinking.
In modern education, tools like MathPapa have made learning algebra easier by providing step-by-step solutions, but understanding the core concepts remains essential.
This comprehensive guide explores algebra in detail, covering all major types with formulas and examples.

What Is Algebra?
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that uses letters (variables) to represent unknown numbers and describes relationships using equations and expressions.
Basic Components of Algebra
- Variables: Symbols representing unknown values (x, y, z)
- Constants: Fixed numerical values
- Expressions: Combinations of variables and constants
- Equations: Mathematical statements showing equality
- Functions: Rules that assign one output to each input
Example
x+5=12
Solving:x=12−5=7
Pre Algebra: The Foundation of Algebraic Thinking
Pre algebra prepares students for formal algebra by strengthening arithmetic skills and introducing variables.
Key Topics in Pre Algebra
- Integers and whole numbers
- Fractions and decimals
- Ratios and percentages
- Powers and roots
- Simple equations
Example (Pre Algebra Equation)
x+3=10
Solution:x=7
Importance of Pre Algebra
Pre algebra builds confidence and ensures students understand number operations before progressing to algebra 1.
Algebra 1: Core Concepts and Skills
Algebra 1 introduces formal algebraic techniques used throughout mathematics.
Major Topics in Algebra 1
- Linear equations
- Inequalities
- Polynomials
- Factoring
- Coordinate geometry
- Systems of equations
Linear Equation Example
2x+4=12
Solution:2x=8⇒x=4
Graphing Linear Equations
Standard form:y=mx+c
Where:
- m = slope
- c = y-intercept
Example
y=2x+1
This line increases by 2 units for every 1 unit increase in x.
Algebra 2 (Algebra2): Advanced Algebraic Methods
Algebra 2 (often written as algebra2) expands on algebra 1 and prepares students for higher mathematics.
Topics Covered in Algebra 2
- Quadratic equations
- Polynomial functions
- Exponents and logarithms
- Rational expressions
- Sequences and series
- Complex numbers
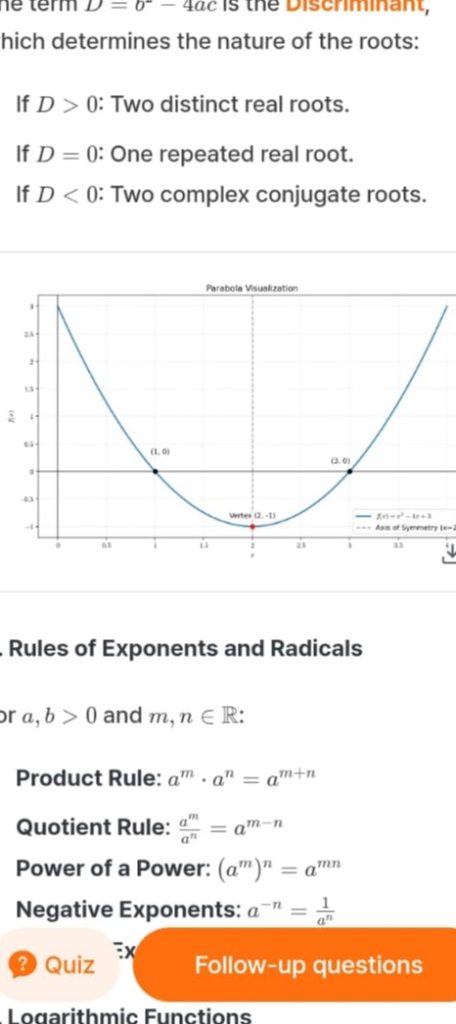
Quadratic Formula
For:ax2+bx+c=0
Solution:x=2a−b±b2−4ac
Example
x2−5x+6=0
Factoring:(x−2)(x−3)=0⇒x=2,3
Linear Algebra: Vectors, Matrices, and Systems
Linear algebra is a powerful branch of algebra used extensively in engineering, computer science, data science, and artificial intelligence.
Key Concepts of Linear Algebra
- Vectors
- Matrices
- Determinants
- Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
- Linear transformations
Matrix Example
A=[1324]
Matrix Addition
A+B=[1324]+[5768]=[610812]
Applications of Linear Algebra
- Machine learning
- Computer graphics
- Electrical engineering
- Network analysis
Boolean Algebra (Algebra Boole)
Algebra Boole, also known as Boolean algebra, is the mathematical foundation of digital electronics and computer logic.
Boolean Values
- 0 (False)
- 1 (True)
Boolean Operations
- AND (·)
- OR (+)
- NOT (¯)
Boolean Laws
- A+0=A
- A⋅1=A
- A+A=A
- A⋅A=A
Example
A⋅(A+B)=A
Applications
- Logic gates
- Computer circuits
- Programming conditions
Binary Algebra: Mathematics of Binary Systems
Binary algebra operates using base-2 numbers (0 and 1), forming the foundation of digital computing.
Binary Numbers
- Decimal 5 = Binary 101
- Decimal 10 = Binary 1010
Binary Addition Example
101+011=1000
Binary Multiplication
101×10=1010
Uses of Binary Algebra
- Computer processors
- Data storage
- Communication systems
Magma Algebra: The Simplest Algebraic Structure
Magma algebra is the most basic algebraic structure in abstract algebra.
Definition
A magma is a set equipped with a single binary operation.
Properties
- Closure only
- No identity required
- No associativity required
Example
Let:M={1,2,3}
Define operation:a∗b=(a+b)mod3
This system forms a magma.
Importance of Magma Algebra
- Foundation of group theory
- Used in abstract algebra research
Difference Between Algebra Types
| Type | Focus | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pre Algebra | Arithmetic foundations | School mathematics |
| Algebra 1 | Linear equations | Daily problem-solving |
| Algebra 2 | Quadratics, functions | Higher math |
| Linear Algebra | Matrices, vectors | Engineering, AI |
| Boolean Algebra | Logic operations | Digital electronics |
| Binary Algebra | Base-2 arithmetic | Computers |
| Magma Algebra | Abstract structures | Advanced theory |
Role of MathPapa in Learning Algebra
MathPapa is a popular online algebra solver that helps students check their solutions.

Advantages
- Step-by-step solutions
- Helpful for algebra 1 and algebra 2
- Quick equation solving
Limitation
MathPapa is a tool, not a replacement for conceptual understanding.
Real-World Applications of Algebra
- Finance: Interest and investment calculations
- Physics: Motion and force equations
- Engineering: Circuit analysis
- Computer Science: Algorithms and logic
- Economics: Demand and supply models
Tips to Master Algebra
- Understand concepts, not memorization
- Practice daily
- Use graphs and visual aids
- Solve word problems
- Verify answers using tools like MathPapa
Conclusion
Algebra is more than just equations; it is a universal language of problem-solving. From pre algebra to algebra 1, algebra 2, linear algebra, and advanced systems like algebra Boole, binary algebra, and magma algebra, algebra equips learners with skills essential for academic and professional success.
Mastering algebra opens doors to science, technology, engineering, economics, and beyond. With consistent practice, clear understanding, and the right resources, algebra becomes not only manageable—but enjoyable.
