Preparing for an electrical interview can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to anticipating the types of technical questions that may be asked.
Acing an interview requires not only a strong grasp of electrical engineering principles but also the ability to effectively communicate your skills and experiences.

Understanding the most common electrical interview questions can significantly boost your confidence and performance during the actual interview.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the types of questions commonly asked in EE interviews.
- Review key electrical engineering concepts and principles.
- Practice problem-solving skills to tackle technical questions.
- Familiarize yourself with the company’s specific requirements.
- Prepare to provide specific examples from your experience.
The Landscape of Electrical Engineering Interviews
As technology advances, the landscape of electrical engineering interviews is becoming increasingly complex. The hiring process for electrical engineers now involves a multifaceted evaluation of both technical competencies and soft skills.
Current Trends in EE Hiring
The electrical engineering job market is witnessing a significant shift towards specialized skills, driven by emerging technologies such as IoT, AI, and renewable energy. Technical recruiters are looking for candidates who not only possess a strong foundation in electrical engineering principles but also have experience with the latest tools and technologies.
What Technical Recruiters Are Looking For
Technical recruiters in the EE field are seeking candidates with a blend of technical expertise and interpersonal skills. The key areas of focus include:
Technical Competencies
- Proficiency in circuit analysis and design
- Knowledge of electronic devices and systems
- Understanding of control systems and signal processing
- Experience with relevant software tools and programming languages
Soft Skills and Team Fit
In addition to technical skills, recruiters are looking for candidates with strong problem-solving abilities, effective communication skills, and the ability to work collaboratively in a team. Soft skills are becoming increasingly important in the hiring process for EE positions.
To succeed in electrical engineering interviews, candidates must demonstrate a balance of technical knowledge and interpersonal skills. By understanding the current trends and recruiter expectations, candidates can better prepare themselves for the challenges of the EE interview process.
Essential Preparation Strategies for Electrical Engineering Interview
Electrical engineering interviews demand a comprehensive preparation strategy that includes technical review, portfolio development, and mock interviews. To succeed, candidates must be well-prepared to tackle a range of questions, from fundamental electrical engineering concepts to advanced topics specific to their area of expertise.

Technical Knowledge Review
A thorough review of technical knowledge is foundational to acing an EE interview. This involves revisiting core concepts such as circuit theory, electromagnetic principles, and power systems. Candidates should also focus on areas relevant to their specialization or the job description.
Recommended Resources and References
To facilitate a comprehensive technical review, candidates can utilize a variety of resources, including textbooks on electrical engineering, online courses, and professional journals. Some recommended texts include “Electrical Engineering: Principles and Applications” and resources like the IEEE Xplore Digital Library. Practicing with electrical interview questions and answers can also be beneficial, as can reviewing materials from reputable sources that offer electrical interview questions and answers pdf.
Mock Interview Practice
Mock interviews are a valuable tool for preparing for the actual interview. They help candidates become familiar with the interview format, practice answering common EE interview questions, and improve their ability to articulate complex technical concepts under time pressure.
Portfolio Development Tips
Developing a strong portfolio is crucial for demonstrating practical skills and experience. Candidates should curate their portfolio to showcase relevant projects, including design challenges and problem-solving scenarios. This not only highlights technical competence but also shows the ability to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems.
By focusing on these preparation strategies, EE candidates can significantly enhance their chances of success in interviews.
Fundamental EE Interview Questions and Answers
To succeed in an EE interview, it’s essential to have a strong foundation in circuit theory, electromagnetic principles, and basic power concepts. These fundamental areas form the core of Electrical Engineering and are frequently tested in interviews.
Circuit Theory Fundamentals
Circuit theory is a crucial aspect of Electrical Engineering, dealing with the analysis of electrical circuits. It involves understanding various laws and techniques used to analyze and design circuits.
Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws
Ohm’s Law relates the voltage across a conductor to the current flowing through it, given a constant resistance. Kirchhoff’s Laws, on the other hand, provide a means to analyze complex circuits by considering the conservation of charge and energy. Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) states that the sum of currents entering a node is equal to the sum of currents leaving the node, while Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) states that the sum of voltage changes around a closed loop is zero.
Resistive networks are circuits composed of resistors and voltage sources. Analyzing these networks involves applying Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws to determine voltages and currents throughout the circuit. Techniques such as series and parallel reduction and mesh analysis are commonly used.
Electromagnetic Principles
Electromagnetic principles are vital in understanding how electrical systems interact with magnetic fields. This includes concepts such as electromagnetic induction, magnetic circuits, and the behavior of inductors and capacitors in circuits.
Basic Power Concepts
Basic power concepts in Electrical Engineering involve understanding how power is calculated and managed in electrical circuits. This includes concepts such as real power, reactive power, and apparent power, as well as power factor correction techniques.
Circuit Analysis and Design Questions
Understanding circuit analysis and design is vital for electrical engineers, as it forms the backbone of many interview questions that evaluate problem-solving skills. Circuit analysis involves examining the behavior of electrical circuits under various conditions, while design focuses on creating circuits that meet specific requirements.
AC Circuit Analysis
AC circuit analysis is a fundamental aspect of electrical engineering, dealing with circuits that involve alternating current. Candidates should be familiar with analyzing circuits using phasors and complex numbers.
Phasors and Complex Power
Phasors simplify the analysis of AC circuits by representing sinusoidal voltages and currents as complex numbers. Understanding complex power, including real and reactive power, is crucial for assessing circuit behavior.
Passive and Active Filters
Filters are critical in signal processing, used to manipulate signal frequencies. Candidates should understand the design and analysis of both passive and active filters, including their applications and limitations.
Resonance and Q-Factor
Resonance occurs when a circuit’s inductive and capacitive reactances are equal, leading to maximum energy transfer. The Q-factor measures the circuit’s quality, indicating its efficiency and selectivity.
Transient Response Analysis
Transient response analysis involves studying how circuits behave during changes, such as switching on or off. Understanding transient responses is essential for designing circuits that can handle sudden changes without malfunctioning.
In conclusion, circuit analysis and design questions are pivotal in electrical engineering interviews. Candidates should prepare by practicing a variety of problems and reviewing fundamental concepts to demonstrate their competence effectively.
Electronics and Semiconductor Device Questions
The realm of electronics and semiconductor devices is vast and intricate, requiring a deep understanding for electrical engineers to excel in their interviews. This section delves into the critical areas of electronics that are commonly tested.

Diode Circuits and Applications
Diode circuits are fundamental in electronic devices, serving various purposes such as rectification, voltage regulation, and signal modulation. Understanding the characteristics of different types of diodes, including their I-V curves and applications, is crucial.
- Rectifier Diodes: Used for converting AC to DC.
- Zener Diodes: Utilized for voltage regulation.
- Schottky Diodes: Known for their fast switching times.
Transistor Biasing and Amplifiers
Transistors are pivotal in electronic circuits, acting as amplifiers or switches. Proper biasing is essential for stable operation.
The biasing of transistors involves setting the appropriate voltage and current levels to ensure they operate within the desired region.
BJT vs. MOSFET Characteristics
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) and Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
| Characteristics | BJT | MOSFET |
|---|---|---|
| Current Control | Current-controlled | Voltage-controlled |
| Input Impedance | Low | High |
| Switching Speed | Moderate | Fast |
Operational Amplifier Configurations
Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are versatile components used in a variety of configurations, including inverting and non-inverting amplifiers, voltage followers, and comparators.
Digital Logic and Boolean Algebra
Digital logic is the foundation of digital electronics, involving the use of Boolean algebra to design and analyze digital circuits.
- Basic Logic Gates: AND, OR, NOT.
- Universal Gates: NAND, NOR.
- Boolean Laws: Used for simplification and manipulation of digital expressions.
Power Systems and High Voltage Engineering
Power systems and high voltage engineering form a critical component of electrical engineering interviews. These topics assess a candidate’s understanding of complex electrical systems, including generation, transmission, and distribution.
Generation and Transmission Concepts
Generation and transmission are fundamental aspects of power systems. Candidates should be familiar with different generation methods, including renewable energy sources and traditional fossil fuel-based systems. Transmission line design, including line parameters and power transfer capability, is also crucial.
Protection Systems and Relays
Protection systems are vital for maintaining the integrity of power systems. Knowledge of protective relays, their operation, and coordination is essential. This includes understanding distance protection, differential protection, and overcurrent protection.

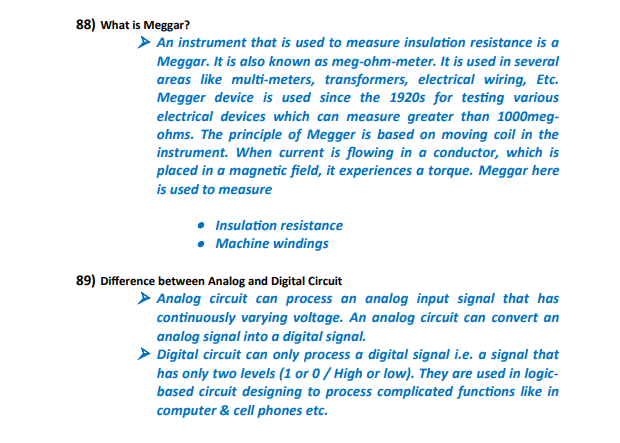
Power Factor Correction
Power factor correction is a technique used to improve the efficiency of power systems. It involves compensating for the reactive power component, thereby reducing the strain on the system. Candidates should understand the methods and benefits of power factor correction.
Fault Analysis and System Stability
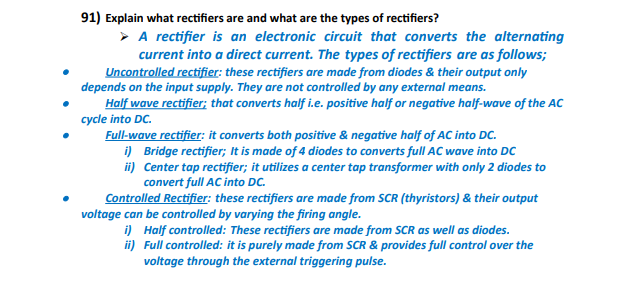
Fault analysis is critical for designing and operating reliable power systems. This includes understanding symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults, as well as techniques for analyzing and mitigating their impact. System stability, including transient stability and steady-state stability, is also a key area of focus.
By mastering these topics, electrical engineering candidates can demonstrate their expertise in power systems and high voltage engineering, enhancing their prospects in interviews.
Control Systems and Automation Questions
In the realm of electrical engineering, control systems and automation play a pivotal role, and being proficient in these areas can significantly enhance a candidate’s chances in job interviews. Control systems are integral to numerous applications, from simple household appliances to complex industrial machinery.
Transfer Functions and System Modeling
Understanding transfer functions is crucial for analyzing and designing control systems. A transfer function represents the relationship between the input and output of a system. Candidates should be prepared to:
- Derive transfer functions for given systems
- Analyze system stability using transfer functions
- Design controllers based on transfer function models
PID Control Design
PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers are widely used in control systems. Interview questions may cover:
- Tuning PID parameters for optimal performance
- Understanding the effects of P, I, and D components
- Implementing PID control in various systems
Stability Analysis Methods
Stability is a critical aspect of control systems. Candidates should be familiar with:
- Routh-Hurwitz criterion
- Nyquist stability criterion
Root Locus and Bode Plots
Root locus and Bode plots are graphical techniques used for stability analysis. Candidates may be asked to:
- Sketch root locus plots for given systems
- Interpret Bode plots to determine stability margins
State-Space Representation
State-space representation is an alternative method for modeling control systems. Candidates should understand how to:
- Convert transfer functions to state-space models
- Analyze system controllability and observability
- Design state feedback controllers
Mastering these concepts is essential for success in control systems and automation interviews. By understanding transfer functions, PID control, stability analysis, and state-space representation, candidates can demonstrate their ability to design and analyze complex control systems.
Digital Signal Processing Interview Topics
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) is a critical area of study in Electrical Engineering, and understanding its concepts is crucial for success in EE interviews. DSP involves the analysis and manipulation of signals to extract or modify information, and it’s a fundamental aspect of many modern technologies.

To excel in DSP-related interview questions, candidates must demonstrate a strong grasp of several key concepts. These include the principles of sampling theory, the design of digital filters, the application of Fourier and Z-transforms, and the practical applications of DSP in real-world systems.
Sampling Theory and Nyquist Criterion
Sampling theory is a cornerstone of DSP, dealing with the conversion of continuous-time signals into discrete-time signals. The Nyquist criterion is a critical concept within sampling theory, dictating that the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency component of the signal to avoid aliasing.
Digital Filters Design
Digital filters are used to manipulate signals in the digital domain, allowing for the removal of unwanted frequency components or the enhancement of desired signals. The design of digital filters involves choosing the appropriate filter type (FIR or IIR), determining the filter order, and calculating the filter coefficients.
Fourier and Z-Transforms
The Fourier transform is a powerful tool for analyzing signals in the frequency domain, while the Z-transform is its discrete-time counterpart. Understanding these transforms is essential for analyzing and designing DSP systems.
Practical DSP Applications
DSP has a wide range of practical applications, from audio processing and image enhancement to telecommunications and biomedical signal processing. Familiarity with these applications can help demonstrate a candidate’s ability to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems.
| DSP Concept | Application | Importance in EE Interviews |
|---|---|---|
| Sampling Theory | Data Acquisition Systems | High |
| Digital Filters | Audio Processing | High |
| Fourier Transform | Spectral Analysis | High |
| Z-Transform | Discrete-Time System Analysis | Medium |
Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems Questions
Microcontrollers and embedded systems form the backbone of modern electronics, making them a key area of focus in EE interviews. These systems are integral to a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial automation.

Architecture and Memory Organization
Understanding the architecture of microcontrollers is fundamental. This includes knowledge of the CPU, memory types (RAM, ROM, EEPROM), and input/output interfaces. Candidates should be able to explain how memory is organized and managed in embedded systems.
Example: A common interview question might ask to describe the differences between Harvard and Von Neumann architectures, highlighting their implications on performance and design complexity.
Programming and Debugging Techniques
Programming microcontrollers often involves using languages like C or C++. Interviewees should be prepared to discuss their experience with these languages, as well as debugging techniques such as using JTAG or SWD interfaces.
Debugging Example: Candidates might be asked to walk through their process for debugging a firmware issue, including the tools they use and how they isolate problems.
Communication Protocols
Embedded systems frequently use various communication protocols to interact with other devices. Understanding protocols like I2C, SPI, UART, and CAN is crucial.
I2C, SPI, UART, and CAN
- I2C: A multi-master, multi-slave protocol used for short-distance communication.
- SPI: A synchronous serial protocol that offers high-speed data transfer.
- UART: An asynchronous serial protocol commonly used for serial communication.
- CAN: A robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers to communicate.
| Protocol | Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| I2C | Multi-master, multi-slave, synchronous | Interfacing peripherals, EEPROM |
| SPI | Synchronous, high-speed | SD cards, displays, sensors |
| UART | Asynchronous, simple | Serial communication, debugging |
| CAN | Robust, multi-master | Automotive, industrial control |
Real-time Systems Concepts
Real-time systems require predictable and timely responses to events. Candidates should understand concepts like task scheduling, priority inversion, and deadline monotonic scheduling.
Real-time Example: An interview question might ask to design a simple real-time system for a given application, such as a data acquisition system, emphasizing the importance of meeting deadlines.
Common Electrical Interview Questions and Answers
Candidates preparing for EE interviews should focus on reviewing fundamental concepts and practicing problem-solving scenarios. Electrical engineering interviews are designed to assess a candidate’s technical knowledge, problem-solving skills, and ability to work collaboratively in a team.
Technical Problem-Solving Scenarios
Technical problem-solving scenarios are a crucial part of EE interviews. These questions are designed to evaluate a candidate’s ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical problems. For instance, candidates might be asked to design a simple circuit or explain how to troubleshoot a faulty electrical system.
- Design a circuit to control a DC motor using a microcontroller.
- Explain the steps to troubleshoot a short circuit in a complex electrical system.
Project Experience Questions
Project experience questions allow interviewers to assess a candidate’s hands-on experience and ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world projects.
Design Process Explanation
When explaining the design process, candidates should outline their approach, including any research conducted, design decisions made, and how they overcame any challenges encountered during the project.
“The most important thing in design is to understand the requirements and constraints of the project. This understanding guides the entire design process, from conceptualization to implementation.”
Troubleshooting Methodologies
Troubleshooting is a critical skill for electrical engineers. Candidates should be prepared to discuss their approach to identifying and resolving issues in electrical systems or circuits.
| Troubleshooting Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Identify the Problem | Clearly define the issue, including symptoms and any error messages. |
| Isolate the Cause | Use diagnostic tools and techniques to narrow down the possible causes. |
| Implement a Fix | Apply the necessary corrections or repairs. |
| Verify the Solution | Test the system to ensure the problem is resolved. |
Team Collaboration Examples
Team collaboration is essential in electrical engineering. Candidates should be prepared to provide examples of how they have worked effectively with others on projects, including how they handled any conflicts or challenges that arose.
Industry-Specific electrical interview questions
Electrical engineering interviews can vary significantly depending on the industry, with different sectors placing emphasis on different aspects of an engineer’s knowledge and experience. Understanding these industry-specific requirements is crucial for success.
Automotive Electronics
In the automotive sector, EE interview questions often focus on embedded systems, automotive communication protocols like CAN and LIN, and safety standards such as ISO 26262. Candidates may be asked to design or troubleshoot automotive electronic systems.
Aerospace and Defense Systems
Aerospace and defense interviews typically cover topics related to high-reliability electronics, radiation-hardened components, and stringent quality control processes. Questions may also delve into system integration, security protocols, and compliance with military standards.
Industrial Automation
For industrial automation, EE interviews often emphasize control systems, SCADA systems, and industrial communication protocols. Candidates may be tested on their knowledge of PLCs, motor control, and safety protocols in industrial environments.
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, interview questions frequently revolve around user interface design, power management, and miniaturization of electronic components. Engineers may be asked about their experience with consumer electronics standards and regulations.
Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy system interviews focus on power electronics, energy conversion, and grid integration. Candidates may be questioned on their understanding of solar inverters, wind turbine control systems, and energy storage technologies.
By familiarizing themselves with these industry-specific EE interview questions, electrical engineers can better prepare for the challenges they will face in their chosen field.
Entry-Level vs. Experienced Electrical Interview Questions Differences
The expectations and challenges in electrical interview questions evolve as one gains experience. For fresh graduates, the focus is on foundational knowledge and potential, while experienced professionals are assessed on their technical expertise, problem-solving skills, and leadership abilities.

Fresh Graduate Expectations
For entry-level electrical interview questions positions, interview questions typically revolve around basic circuit theory, electronic devices, and fundamental power concepts. Candidates are expected to demonstrate a solid understanding of their undergraduate coursework and any relevant projects they’ve worked on.
Key areas of focus include:
- Circuit analysis and design
- Electronic devices and circuits
- Basic power systems
- Problem-solving skills
Mid-Career Technical Depth
As engineers gain experience, the interview questions become more challenging, delving into advanced topics such as control systems, digital signal processing, and specialized areas relevant to the company’s focus.
Mid-career candidates are expected to:
- Demonstrate in-depth knowledge of their specific domain
- Showcase their problem-solving skills with complex technical problems
- Highlight their experience with relevant technologies and tools
Senior Engineer Leadership Questions
For senior EE positions, the interview process often includes questions that assess leadership skills, project management experience, and the ability to mentor junior engineers.
Senior candidates are expected to:
- Discuss their experience in leading projects and teams
- Demonstrate their ability to make strategic technical decisions
- Showcase their understanding of industry trends and future directions
Specialized Knowledge Assessment
Regardless of experience level, candidates may be assessed on specialized knowledge relevant to the company’s specific needs, such as expertise in renewable energy systems, automotive electronics, or other niche areas.
The assessment may include:
- Technical interviews with domain experts
- Practical problem-solving exercises
- Review of past projects and experiences
Practical and Hands-on Interview Challenges
EE interviews typically involve a mix of theoretical questions and practical, hands-on challenges. These challenges are designed to assess a candidate’s ability to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Circuit Troubleshooting Scenarios
Circuit troubleshooting is a critical skill for electrical engineers. Candidates may be presented with a faulty circuit and asked to identify the issue and propose a solution. For instance, they might be given a circuit with an unexpected output voltage and be required to diagnose the problem using measurement tools and circuit analysis techniques.
- Identify the faulty component or connection.
- Use multimeters and oscilloscopes to measure circuit parameters.
- Apply circuit analysis techniques, such as Kirchhoff’s laws, to diagnose the issue.
Design Challenges and Case Studies
Design challenges are another common aspect of practical EE interviews. Candidates might be asked to design a circuit or system to meet specific requirements, such as a power supply with certain voltage and current ratings. They may need to select appropriate components, justify their design choices, and discuss potential trade-offs.
Key considerations in design challenges include:
- Meeting the specified performance requirements.
- Selecting components that are available and cost-effective.
- Ensuring the design is robust and reliable.
Equipment and Tool Knowledge
Familiarity with common EE equipment and tools is essential. Candidates may be asked about their experience with tools like oscilloscopes, signal generators, and PCB design software. They should be prepared to discuss how they’ve used these tools in previous projects or internships.
Code Review and Debugging Tasks
For EE roles involving programming, code review and debugging are critical skills. Candidates may be given a piece of code with errors or inefficiencies and asked to identify and fix the issues. They should be able to explain their thought process and the steps they take to debug the code.
By understanding these practical and hands-on interview challenges, EE candidates can better prepare themselves for the types of questions and tasks they’ll face in their interviews.
Conclusion
Acing an electrical engineering interview requires a combination of technical knowledge, problem-solving skills, and confidence. Throughout this article, we’ve explored various aspects of electrical interview questions preparation, from fundamental concepts to industry-specific questions.
To excel in your EE interview, focus on reinforcing your technical foundation, practicing problem-solving scenarios, and reviewing industry trends. Effectiveelectrical interview questions preparation involves not just studying technical concepts, but also demonstrating your ability to apply them in real-world situations.
As you prepare, consider the types of electrical interview question tips that can help you stand out, such as showcasing your projects, being ready to discuss your design decisions, and demonstrating your understanding of current technologies and innovations in the field.
By combining thorough preparation with confidence and clear communication, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle your EE interview and take a significant step towards your career goals.
FAQ
What are the most common types of EE interview questions?
The most common types of EE interview questions cover circuit theory, electronics, power systems, control systems, and digital signal processing, as well as practical problem-solving scenarios and project experience.
How should I prepare for an EE interview?
To prepare for an EE interview, review technical knowledge, practice with mock interviews, and develop a professional portfolio showcasing relevant projects and experiences.
What technical competencies are recruiters looking for in EE candidates?
Recruiters look for technical competencies such as circuit analysis, electronics, and programming skills, as well as knowledge of industry-specific technologies and trends.
How important are soft skills in EE interviews?
Soft skills, such as teamwork, communication, and problem-solving, are crucial in EE interviews as they demonstrate a candidate’s ability to work effectively in a team and adapt to new challenges.
What are some common EE interview questions related to circuit analysis?
Common EE interview questions related to circuit analysis include AC circuit analysis, filter design, resonance, and transient response, as well as circuit troubleshooting scenarios.
How can I improve my chances of success in an EE interview?
To improve your chances of success, thoroughly prepare by reviewing technical knowledge, practicing with mock interviews, and showcasing relevant projects and experiences.
What are some industry-specific EE interview questions?
Industry-specific EE interview questions vary by sector, such as automotive electronics, aerospace, industrial automation, consumer electronics, and renewable energy systems, and may cover specialized technologies and applications.
How do EE interviews differ for entry-level versus experienced candidates?
EE interviews for entry-level candidates focus on foundational technical knowledge and potential, while experienced candidates are assessed on technical depth, leadership skills, and specialized knowledge.
What types of practical challenges can I expect in an EE interview?
Practical challenges in EE interviews may include circuit troubleshooting, design challenges, equipment knowledge, and code review tasks, which test a candidate’s hands-on skills and problem-solving abilities.
How can I demonstrate my problem-solving skills in an EE interview?
To demonstrate problem-solving skills, be prepared to tackle technical problem-solving scenarios, explain your design process, and showcase troubleshooting methodologies.
What is the importance of reviewing fundamental EE concepts?
Reviewing fundamental EE concepts, such as circuit theory, electronics, and power systems, is crucial to success in EE interviews, as it demonstrates a strong foundation in electrical engineering principles.